
Relational database management system (RDBMS) is the backbone of modern-day data storage and retrieval systems. It is a software program that allows users to define, create, maintain, and manipulate relational databases. RDBMS ensures consistency, accuracy, and security of data while providing easy access to it whenever required. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of RDBMS and understand its fundamentals.
RDBMS is a type of database management system (DBMS) that uses a set of tables to store, retrieve, and organize data. It follows a relational model where each table in the database is related to one or more tables through a common field. The relationships between these tables allow for efficient and structured management of data.
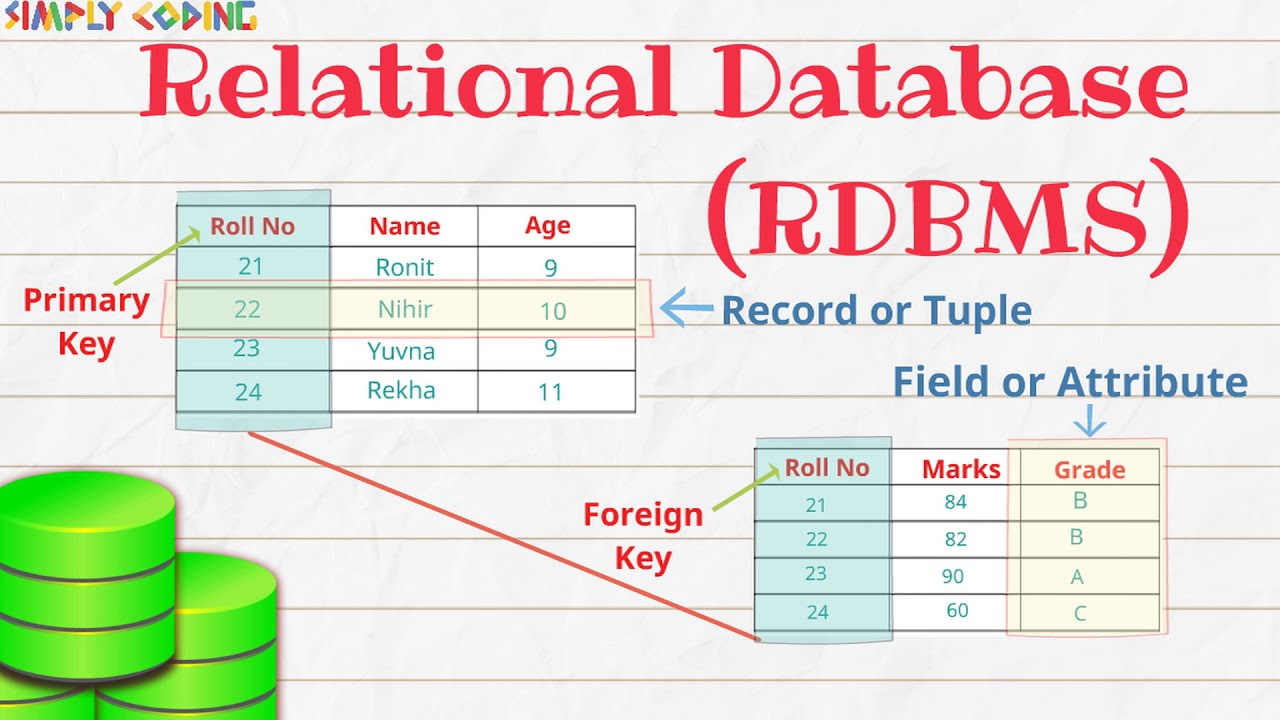
RDBMS works by organizing data into tables with predefined columns and rows. Each column represents an attribute, while each row represents a record. Each table in the database has a primary key that uniquely identifies each record. The relationships between tables are established using foreign keys that reference the primary key of another table. This allows RDBMS to combine data from multiple tables into a single query result, facilitating complex data analysis and reporting.
Most organizations are at the least experimenting with cloud workloads, however many even have a really combined cloud surroundings. Of the organizations working cloud workloads, we estimate at the least 80 % have a multi-cloud surroundings that features entry to each on-prem and public cloud cases, in addition to utilizing a number of suppliers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google, Oracle, IBM, SAP, and many others.). This makes the world of cloud deployments very complicated.
RDBMS offers several benefits over other database management systems. Some of the most significant benefits are:
RDBMS ensures data consistency by enforcing constraints on the data entered into the database. This means that only valid data is stored in the database, ensuring accurate results when queried.
Data security is another significant advantage of RDBMS. It provides strict access controls and user permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access the data.
RDBMS is highly scalable and can manage large datasets effectively. It allows for horizontal and vertical scaling, making it a suitable choice for businesses with growing data requirements.
RDBMS provides easy maintenance and management of databases. It offers tools to backup, restore, and recover data in case of failures or disasters.

Using RDBMS involves several steps that must be followed to create, maintain, and manage a database. The following are the typical steps involved in using RDBMS:
Some popular examples of RDBMS include:
Oracle is one of the most widely used commercial RDBMS systems. It supports various platforms and offers advanced features such as partitioning, replication, and clustering.
MySQL is an open-source RDBMS system that is widely used for web applications. It is easy to use, scalable, and offers various storage engines to choose from.
Microsoft SQL Server is a commercial RDBMS system that runs on Windows. It offers high availability, disaster recovery, and business intelligence features.
RDBMS is not the only type of DBMS available. Other types of DBMS include NoSQL, Object-Oriented DBMS, and Graph DBMS. The following are some comparisons between RDBMS and other DBMS:
RDBMS uses a structured schema with fixed fields and relationships, while NoSQL uses an unstructured schema with dynamic fields. NoSQL is more suitable for handling unstructured data such as documents, images, and videos.
Object-Oriented DBMS uses objects to represent data instead of tables. It is more suitable for applications that require complex data structures and inheritance relationships.
Graph DBMS use graph structures to represent data, making it easier to represent complex relationships. It is suitable for applications that require analysis of relational data.
When using RDBMS, the following tips can help improve its efficiency:
Normalize the database by removing redundant data and organizing it into separate tables. This improves data consistency and reduces storage requirements.
Use indexing to improve query performance by creating indexes on frequently queried columns. This reduces the time required to search for data and improves database performance.
Optimize queries by using appropriate query optimization techniques such as using indexes, avoiding subqueries, and avoiding unnecessary joins. This improves query performance and reduces the load on the database server.
Perform regular backups of the database and implement a disaster recovery plan in case of any failures or disasters. This ensures that data is not lost and can be recovered in case of any unforeseen circumstances.
Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a powerful tool for organizing and managing structured data. It offers several benefits over other DBMS systems, including data consistency, better security, scalability, and easy maintenance. By following best practices and optimizing queries, RDBMS can offer high-performance capabilities for large-scale data management and analysis.
In conclusion, RDBMS is an essential tool for businesses that require efficient and organized data management. Its ability to combine data from multiple tables and provide meaningful insights makes it an indispensable tool for data analysts and developers. With its popularity and widespread usage, RDBMS remains a critical component of modern-day data storage and retrieval systems.