
Private public cloud hybrid is a buzzword in the world of cloud computing. The concept of a hybrid cloud is gaining popularity, as it offers the benefits of both private and public clouds. In this article, we will explore what private, public, and hybrid clouds are, their differences, benefits, and drawbacks. We will also provide some case studies, comparisons, and advice on adopting a private public cloud hybrid.
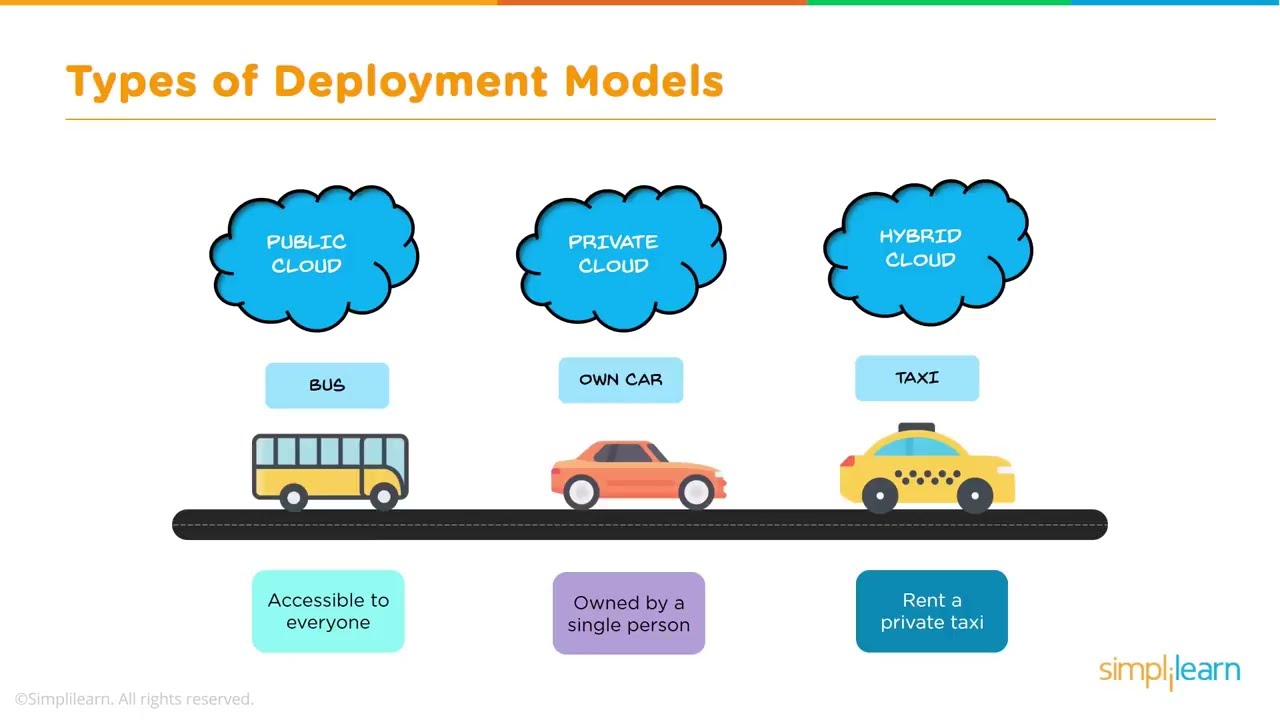
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment that is used exclusively by an organization. It is not shared with other organizations or individuals and is typically hosted on-premises or in a data center that is owned or leased by the organization. A private cloud provides greater control over security, compliance, and performance but requires significant investment in hardware, software, and maintenance.
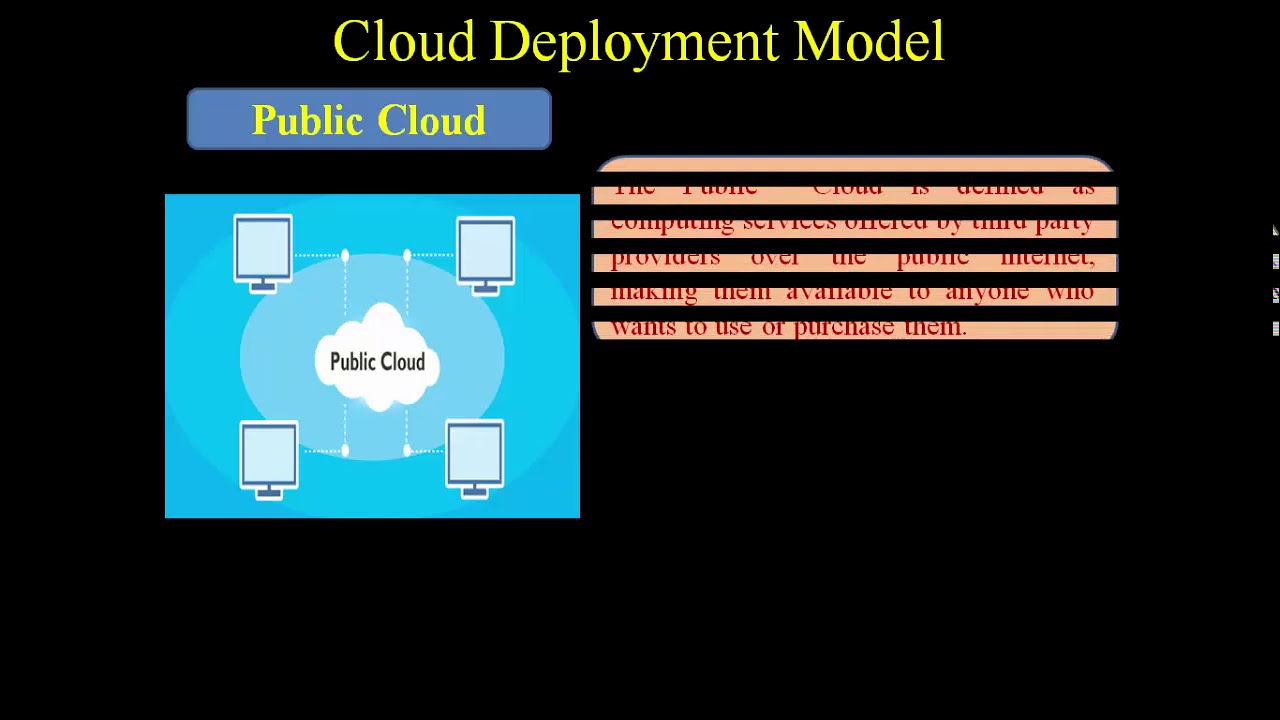
A public cloud is a cloud computing environment that is provided by a third-party service provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The infrastructure and resources of a public cloud are shared among multiple organizations or individuals. A public cloud provides greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness but may have limitations on security, compliance, and customization.
Certainly, Pink Hat is the main Linux-based supplier of enterprise cloud infrastructure. It’s been adopted by 90 % of enterprises and has greater than 8M builders. Its OpenShift expertise is a key part of its success, because it gives a solution to simply deploy multi-cloud environments by a full stack management and administration functionality constructed on prime of business normal Kubernetes and deployed in a digital Linux stack.
A hybrid cloud is a combination of private and public clouds. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both cloud models while addressing their specific requirements. A hybrid cloud can be configured in various ways, such as connecting a private cloud to a public cloud, using multiple public clouds, or using multiple private clouds. A hybrid cloud provides greater flexibility, agility, and cost optimization but requires expertise in managing and integrating multiple environments.

Netflix is a global streaming service that uses a hybrid cloud model to deliver its content. It has a large private cloud infrastructure that hosts its critical services, such as customer data, billing, and recommendations. It also uses multiple public clouds, such as AWS, GCP, and Azure, to support its streaming and storage needs. The hybrid cloud architecture allows Netflix to scale up or down based on demand, optimize costs, and ensure high availability and resilience.
NASA is a federal agency that uses a hybrid cloud model to support its mission-critical operations. It has a private cloud infrastructure that hosts its sensitive data and applications, such as satellite imagery and scientific simulations. It also uses multiple public clouds, such as AWS and GCP, to support its research and development projects. The hybrid cloud architecture allows NASA to leverage specialized cloud services, such as machine learning and big data analytics, without compromising security and compliance.
Private clouds offer greater control over security and compliance since they are not shared with other entities. Public clouds may have security and compliance limitations due to their multi-tenant nature. Hybrid clouds can balance security and compliance by hosting sensitive data and applications in a private cloud and using public clouds for non-sensitive workloads.
Private clouds offer better performance and reliability since they are hosted on dedicated hardware and networks. Public clouds may have performance fluctuations and latency issues due to their shared infrastructure. Hybrid clouds can balance performance by using private clouds for mission-critical applications and public clouds for bursty workloads.
Private clouds require significant investment in hardware, software, and maintenance, which may not be cost-effective for small or medium-sized organizations. Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go model that allows organizations to scale up or down based on demand. Hybrid clouds can optimize costs by using private clouds for steady workloads and public clouds for variable workloads.

Before adopting a private public cloud hybrid, assess your business needs, such as security, compliance, performance, scalability, and cost. Identify which workloads are suitable for private clouds, public clouds, or hybrid clouds.
Migrating to a private public cloud hybrid requires careful planning and execution. Define your migration strategy, such as lift-and-shift, re-platforming, or refactoring. Consider the impact on data integration, application compatibility, and user experience.
Selecting the right private and public cloud providers is critical for the success of your hybrid cloud. Evaluate their offerings, pricing, support, and SLAs. Ensure that they have robust security and compliance capabilities.
Managing a private public cloud hybrid requires expertise in cloud orchestration, automation, monitoring, and optimization. Consider using cloud management tools and services to simplify your operations and reduce costs.
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment that is used exclusively by an organization, while a public cloud is a cloud computing environment that is shared among multiple organizations or individuals.
A hybrid cloud is a combination of private and public clouds, while a multi-cloud is the use of multiple public clouds from different providers. A hybrid cloud is designed to provide the benefits of both private and public clouds, whereas a multi-cloud is used to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage specific cloud services.
A private public cloud hybrid can provide significant benefits for small businesses, such as flexibility, scalability, and cost optimization. However, it requires expertise in managing and integrating multiple cloud environments, which may not be feasible for small businesses with limited resources.
To ensure security and compliance in a private public cloud hybrid, implement robust access controls, encryption, monitoring, and auditing. Follow industry standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. Use third-party security and compliance tools, if necessary.
To optimize costs in a private public cloud hybrid, identify your workload patterns and usage trends. Use cost management tools and services to monitor and optimize your spending. Choose the right pricing models, such as reserved instances, spot instances, or on-demand instances. Consider using serverless computing and containerization to reduce infrastructure costs.
Private public cloud hybrid is an innovative approach to cloud computing that combines the benefits of private and public clouds. It allows organizations to achieve greater flexibility, agility, and cost optimization while addressing their specific requirements. By understanding the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of private, public, and hybrid clouds, and following best practices for adoption and management, organizations can successfully adopt a private public cloud hybrid and reap its rewards.